Binary Tree Traversal
In tree traversal, we have pre-order traversal, in-order traversal, post-order traversal and level-order traversal. This post concludes all these traversals’ implementation.
Pre-order Traversal
Given a tree below, the pre-order traversal will be [1, 2, 3].
1 | |
Recursive
1 | |
Iterative
1 | |
In-order Traversal
Recursive
1 | |
Iterative
1 | |
Post-order Traversal
1 | |
Recursive
1 | |
Iterative
Similar to pre-order traversal’s root -> left -> right, this time we traverse root -> right -> left. At the end, we reverse the result list to get left -> right -> root.
1 | |
Lever-order Traversal
1 | |
Iterative
1 | |
Recursive
1 | |
Morris Traversal
We can use morris traversal to traverse in-order, pre-order, post-order in $O(n)$ time, $O(1)$ space.
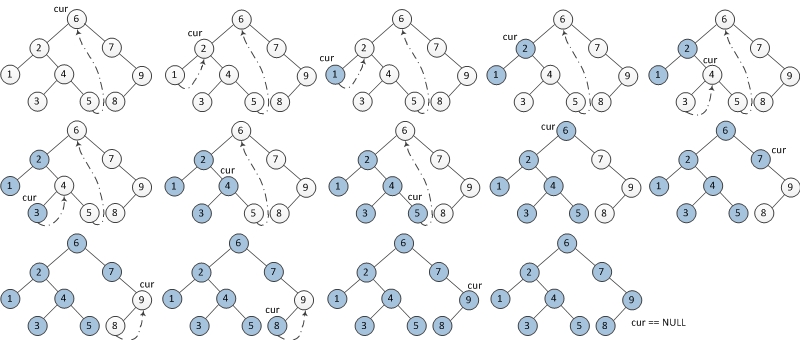
In-order Traversal
- If the current node’s left child is null, print out current node, and its right child becomes current node.
- If the current node’s left child is not null, in current node’s left subtree, find the current node’s in-order traversal predecessor, in other word, find the node before the current node in the order of in-order traversal.
- If the predecessor node’s right child is null, set its right child to current node. Current node’s left child becomes current node.
- If the predecessor node’s right child is current node, set its right child to null. Print out current node. Current node’s right child becomes current node.
- Repeat step 1 and step 2 until current node is null.
1 | |
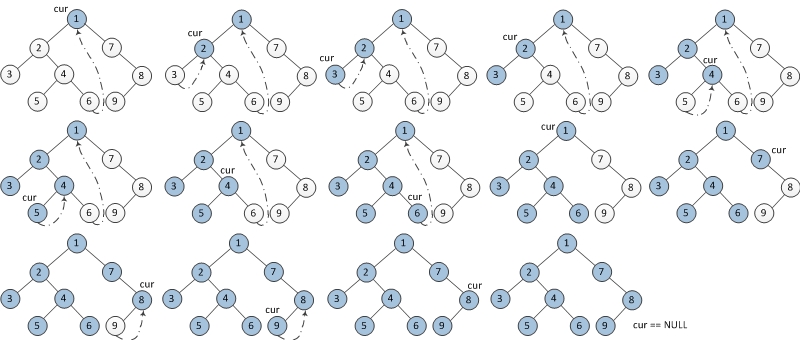
Pre-order Traversal
- If the current node’s left child is null, print out current node, and its right child becomes current node.
- If the current node’s left child is not null, in current node’s left subtree, find the current node’s in-order traversal predecessor.
- If the predecessor node’s right child is null, set its right child to current node. Print out current node. Current node’s left child becomes current node.
- If the predecessor node’s right child is current node, set its right child to null. Current node’s right child becomes current node.
- Repeat step 1 and step 2 until current node is null.
1 | |
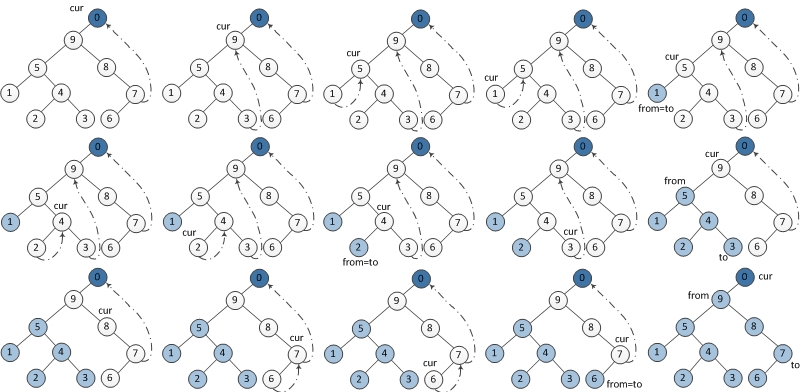
Post-order Traversal
Before we start, we create a dump TreeNode, and make its left child be the root node. Current node set to the dump node.
- If the current node’s left child is null, set its right child becomes current node.
- If the current node’s left child is not null, in current node’s left subtree, find the current node’s in-order traversal predecessor.
- If the predecessor node’s right child is null, set its right child to current node. Current node’s left child becomes current node.
- If the predecessor node’s right child is current node, set its right child to null. Reversly print out all the nodes from the current node’s left child to the predecessor node. Current node’s right child becomes current node.
- Repeat step 1 and step 2 until current node is null.
1 | |
Source: