Problem
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
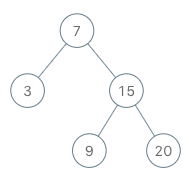
1 | |
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
Explanation
-
In the constructor, we can use in-order traversal iterative way to store the left child elements into a stack.
-
In the
hasNextfunction, we can check if stack is empty. If not empty, then return true. -
In the
nextfunction, we can return the pop node element. Also, we check if that pop node has right child, if it has right child, then we think of that right child is the root, and we push that “root” and all its left nodes to the stack like we did in the step 1.
Solution
1 | |