Problem
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
1 | |

Example 2:
1 | |
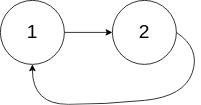
Example 3:
1 | |

Follow-up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
Explanation
- Both slow and fast pointers point to the head.
- While fast and fast.next is not null, when slow pointer moves one step, fast pointer moves two steps.
- If slow pointer and fast pointer points to the same node, then it means there’s cycle, break out of the while loop.
- When out of the while loop, we first check if the fast pointer hits the end, if either fast or fast.next is null, then it means no cycle.
- Now, slow pointer moves back to the head. Fast pointer doesn’t move.
- Then run both, slow pointer and fast pointer at the same speed, the point the meet is the entry of cycle.
Solution
1 | |