Problem
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
1 | |
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
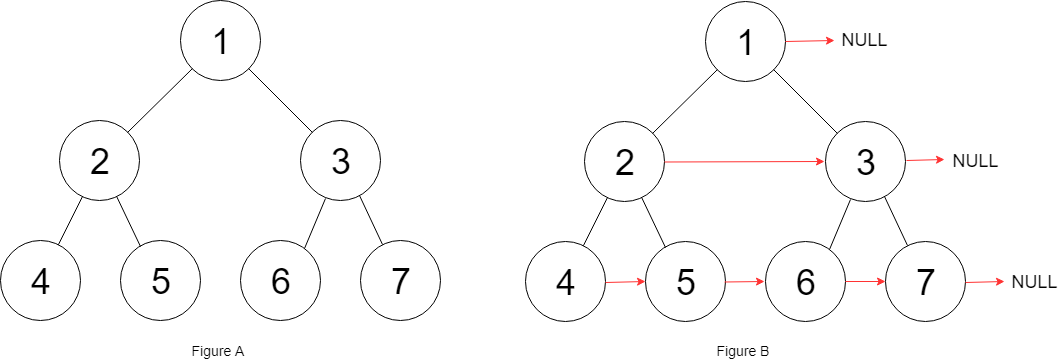
1 | |
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Explanation 1
- We can use recursion method here. Since this is a perfect binary tree, if the root node has left node, then it must has right node, so we can check if it has left node first, then connect it with its right node. To connect the right node’s next node, we first check its parent node has next node, if it has, then we can connect the right node’s next to its parent node’s left node.
Solution 1
1 | |
Explanation 2
- We can use a O(1) space iterative method to solve this problem. We create a
startpointer that points to the current level’s beginning, acurpointer that is used to iterate the current level’s node.
Solution 2
1 | |