Problem
Given a binary tree
1 | |
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
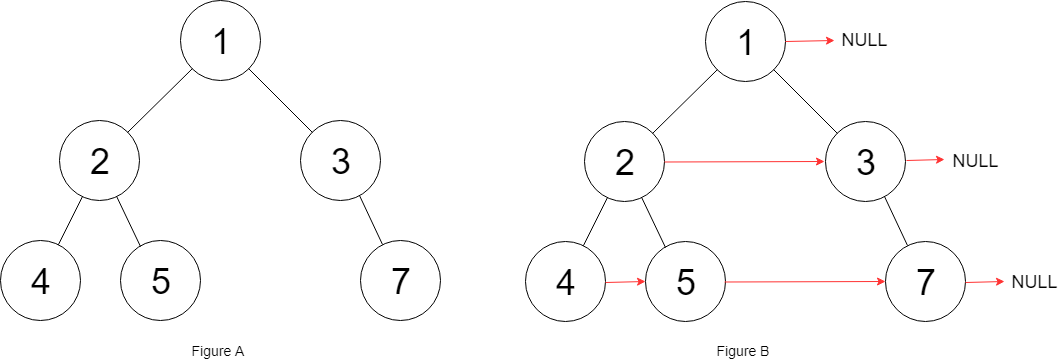
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Explanation 1
-
Similar to 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node, if we want to use recursion method, we can first make a pointer that points to the current node’s next node. Then, we find this pointer’s left most node. And we use the current node’s right node points to that left most node we found, and the current node’s left node points to the current node’s right node like the last problem.
-
Recursivly apply the above method to the current node’s right node and left node. The base case is if the root node is NULL, we can just return.
Solution 1
1 | |
Explanation 2
- This solution uses O(1) space and it is iterating level by level. First, we create a dummy list that is used to pointing to each level’s element before the first element. We create a
curpointer that is used to iterate the current level’s element, it connects its current node’s sub node’s next. First, if the left subnode exists,cur.nextconnects it, then iteratecur = cur.next. If the right subnode exists,cur.nextconnects it, then iteratecur = cur.next. Now, the root’s left and right subnodes are connected. Then, we moverootto the right. After we move, ifrootis not exist, then it means we finish connecting to current root node’s sub node. We then resetrootto dummy’s next node,curreset pointing todummy, and we setdummy’s next to null because we want thecurpointer’s next to NULL so that we can usecur.nextto point to the first element in the next level.
Solution 2
1 | |